- October 27, 2023
- by Kaizen
- Brass Screw, Fasteners and Fixing
What is Lag Screw? Dimensions, Properties and Uses
Have you ever been curious about lag screws and how they vary from ordinary screws? Why are they so adaptable and perfect for many kinds of uses? Large wood screws with a hexagonal or square head used to fasten concrete, metal, wood, and other materials are called lag screws, or lag bolts. They have different lengths and widths, and because of their special qualities, they may be used for a variety of do-it-yourself and building tasks. In order to help you choose the best fastener for your project, we will examine lag screws in more detail in this piece, including their sizes, characteristics, and applications.
What is Lag Screw?
What is Lag Screw? A lag screw is a fastener with a square or hexagonal head and thick, coarse thread. Usually, it is used, either by itself or in conjunction with other screws, to fasten large weights into metal and wood surfaces. Because of the increased friction created by their broad threads between the fastened items, lag screws are intended to grip better than regular wood screws. Additionally, the lag screw needs more energy to push into position, but when done correctly, it forms a very strong link.
Lag Screw Dimensions:
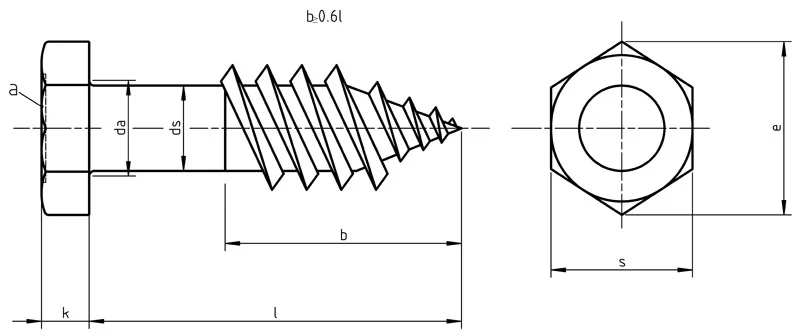
| Hex Lag Screws: Dimensions (ASME B18.2.1-1996) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Product Diameter
Click on the size to shop products |
Threads Per Inch | Body or Shoulder Diameter (E) | Width Across Flats (F) | Width Across Corners (G) | Head Height (H) | Shoulder Length (S) | |||||||
| Max | Min | Basic | Max | Min | Max | Min | Basic | Max | Min | Min | |||
| #10 | .1900 | 11 | .199 | .178 | 9/32 | .281 | .271 | .323 | .309 | 1/8 | .140 | .110 | .094 |
| 1/4 | .2500 | 10 | .260 | .237 | 7/16 | .438 | .425 | .505 | .484 | 11/64 | .188 | .150 | .094 |
| 5/16 | .3125 | 9 | .324 | .298 | 1/2 | .500 | .484 | .577 | .552 | 7/32 | .235 | .195 | .125 |
| 3/8 | .3750 | 7 | .388 | .360 | 9/16 | .562 | .544 | .650 | .620 | 1/4 | .268 | .226 | .125 |
| 7/16 | .4375 | 7 | .452 | .421 | 5/8 | .625 | .603 | .722 | .687 | 19/64 | .316 | .272 | .156 |
| 1/2 | .5000 | 6 | .515 | .482 | 3/4 | .750 | .725 | .866 | .826 | 11/32 | .364 | .302 | .156 |
| 5/8 | .6250 | 5 | .642 | .605 | 15/16 | .938 | .906 | 1.083 | 1.033 | 27/64 | .444 | .378 | .312 |
| 3/4 | .7500 | 4-1/2 | .768 | .729 | 1-1/8 | 1.125 | 1.088 | 1.299 | 1.240 | 1/2 | .524 | .455 | .375 |
| 7/8 | .8750 | 4 | .895 | .852 | 1-5/16 | 1.312 | 1.269 | 1.516 | 1.447 | 37/64 | .604 | .531 | .375 |
Lag Screw Properties:
Lag screws are more dependable and long-lasting than ordinary screws since they are composed of strong steel. Various coatings, such as galvanized, black oxide, zinc plating, and stainless steel, are available for lag screws. These coatings improve the screws’ resistance to weathering, rust, and corrosion depending on the use. Furthermore, lag screws can penetrate deeper into the material and increase resistance to pull-out and shear stresses because of their tapered shank below the thread.
Lag Screw Uses:
There are several applications for lag screws, such as constructing decks, erecting fences, fastening structural elements, and stabilizing large equipment. Their ability to withstand weather makes them perfect for building outside constructions like gazebos, carports, and pergolas. In house remodeling tasks like carpentry and construction, lag screws are also utilized to firmly fasten big, bulky items to walls and roofs.
Lag Screw Installation:
The simple technique of installing lag screws only needs a few tools: a pilot hole drill bit, a socket wrench, and a drill. Drill a pilot hole matching the screw’s diameter and shank size before installing the lag screws. The screw should then be driven into the material using a socket wrench until it is flush with the surface. To avoid overloading or under loading the screw, which can harm the material or compromise its structural integrity, it is imperative to make sure the screw is tightened to the appropriate torque.
Lag Screw Maintenance:
Regular maintenance and inspections are necessary to guarantee the lifespan of lag screws. Periodically check the screws to make sure they are not broken, loose, or rusted. To preserve the integrity of the structure, replace any rusty or corroded screws with new ones.
Conclusion:
Lag screws are a crucial part of DIY and building projects because of their special qualities and adaptability. They are dependable and long-lasting, and they are available in numerous sizes and coatings to meet a range of needs. By being aware of the lag screw’s measurements, characteristics, and applications, you can select the best fastener for your project with knowledge. To guarantee that lag screws function as intended and preserve the structural integrity of the material, install and maintain them in accordance with the suggested procedures.


